Hernia
Internal & External
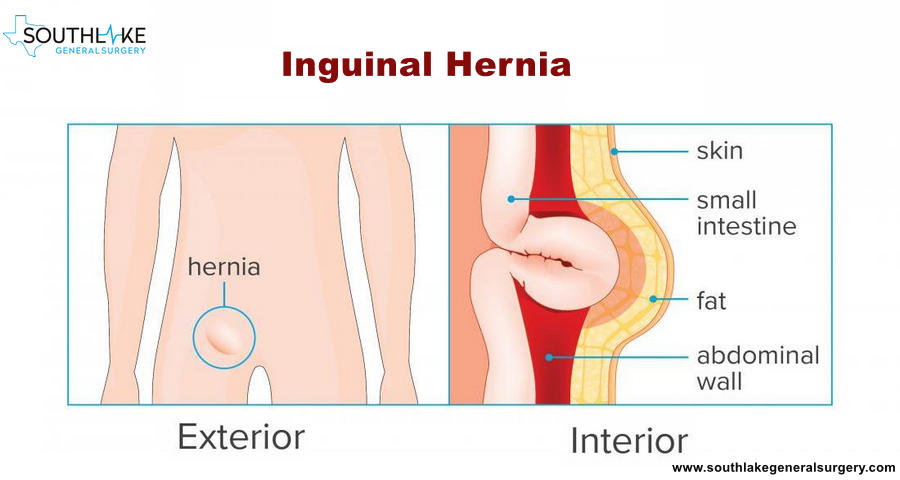
Hernia is the protrusion (bulge) of the abdominal viscera outside the abdominal cavity through a natural or acquired defect.
Commonest types : a) Inguinal b) Femoral c) Umbilical d) Incisional e) Paraumbilical f) Epigastic
Causes:
a) Congenital eg. Indirect Inguinal Hernia.
b) Acquired: Conditions which raise the intra-abdominal pressure e.g: chronic cough, straining at motions in chronic constipation, straining at micturition in enlarged prostate or stricture urethra and person who is heavy weight lifter.
Inguinal Hernia
Indirect Hernia
i) Usually straining is required to bring hernia down.
It does not disappear easily when patient lies down
& little manipulation is required for it to be reduced
ii) Seen in all ages , common in male, only on one side of body.
iii)It always comes out through the external inguinal ring.
Direct Hernia
i) Hernia appears as soon as the patient stands.
It disappears as he lies down.
ii) Seen in elderly. Usually affects both sides of body.
iii) It occasionally come out of the external inguinal ring.
Other Types
a) Enterocele: When the sac contains intestine.
b) Omentocele: When it contains omentum.
c) Enteroomentocele: both intestines & omentum.
d) Cystocele: A portion of the urinary bladder may be in wall of sac.
Treatment
Treatment of Indirect Inguinal hernia:
1) Herniotomy alone : Removal of hernial sac only.
2) Prolene mesh hernioplasty: hernial repair is done by using prolene mesh. As the recurrence is very minimal.
Treatment of Direct Inguinal hernia:
Same as indirect hernia with the exception that the hernial sac need not be removed. For after it has been dissected free from surrounding structures it is inverted into abdomen.
Umbilical Hernia : It is mostly seen in childhood. Pt has swelling in umbilical region which increase during coughing, straining. Treatment is repair of hernia by mesh.
Incisional Hernia:It occurs through a weak scar ( Post-operative hernia)
Paraumbilical Hernia: It occurs either above or below the umbilicus.
Epigastric Hernia: Occurs as small protrusion (swelling) in the midline between xiphoid process & the umbilicus.
Complications
1) Irreducibility: Contents can not be pushed back inside the abdomen.
2) Obstruction
3) Strangulation : When blood supply of the hernial contents is impaired, cause is constriction Band.
4) Gangrene
5) Perforation.
So to prevent the emergency admission and operation, hernial repair should be done as early as possible as elective repair. We perform all types of hernial repair at our centre as a day care procedure.
Postoperative Precaution
1) Do not lift heavy weight for 3 to 6 months.
2) Do not strain during motions.
3) Avoid bike riding for 6 weeks.